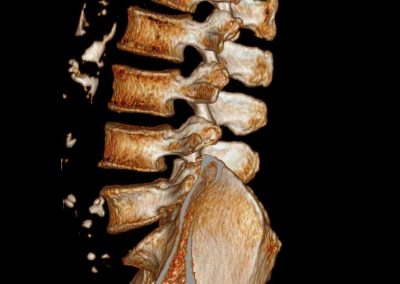
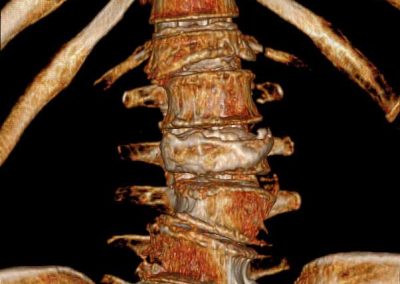
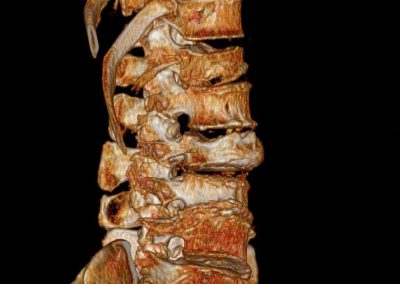
Spinal Fractures
Definition of Spinal Fractures
Symptoms
Small movements and vibrations cause excruciating pain in the fractured spine regions.
Dull, long-lasting night pain and reduction of body height are signs and symptoms of pathological vertebral fractures.
Dull, long-lasting night pain and reduction of body height are signs and symptoms of pathological vertebral fractures.
Treatment
Severe traumatic vertebral fractures require fusion surgery to stabilize the spine and avoid or improve neurological damage. In osteoporotic fractures cement injection into the vertebral body (vertbroplasty, kyphoplasty) stabilizes the vertebral body and reduces pain immediately.
Post-operative course
Patients with severe fractures with neurological damage where complex surgery is indicated require a long rehabilitation process to regain function for every day demands. Neurological improvement may not always occur. Patients without marked neurological damage must stay in the hospital for a short period of time.
Results
Due to the stabilization of the spine the fractures are healed and pain is markably reduced. Unfortunately, paralysis may be permanent and cannot be influenced by surgery.
Revision surgery may be indicated in non-union of the fracture leading to implant failure or angular deformity.
In patients with osteoporotic spinal fractures treated with cement injection pain is diminished immediately. Further fractures though may occur if osteoporosis is not treated medically.
Revision surgery may be indicated in non-union of the fracture leading to implant failure or angular deformity.
In patients with osteoporotic spinal fractures treated with cement injection pain is diminished immediately. Further fractures though may occur if osteoporosis is not treated medically.